Wireless Control Systems
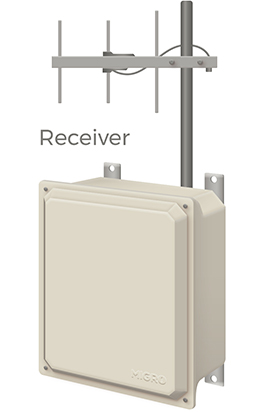
Always keep in mind that there are three parties capable of operating a remote control system: a computerized system, a control signal, or a person. Also, remember that industrial controls and consumer ones work differently. On industrial-grade remotes, the receiver catches the radio signal from the transmitter, and if it matches the security code, goes through a verification process; once that’s one, the receiver activates a relay. This relay, in turn, activates a function that goes from the application coordination to the transmitter signal. In the meantime, the FCC designates a frequency for the system, though it’s worth noting that shorter range applications use different bands.
Migro Xtended Range
You can use the Migro Xtended Range Wireless Control line of receivers and transmitters in a broad variety of remote applications, such as lighting control, SCADA, Race Track Warning Systems, Pump Control, Gate Access, Monitor remote sites, Irrigation Gates, Industrial Monitoring, Alarms, Valves Factory process, PLC remote, and Generators.
Antennas
Since industrial radio controllers couple an electrical connection with the electromagnetic field, all transmitters, and receivers of this grade require antennas. It’s critical to choose the right one depending on the usage, keeping type, and size in mind.
WiFi Controlled
It’s possible to use the Migro Smart Wi-Fi Controller for a broad range of applications, from industrial controls to full home automation. It’s perfectly compatible with the most popular Internet of Things systems, such as Amazon Echo (Alexa), Google Home, and IFTTT. The controller has a 120VAC or 240VAC rating, resisting 50 Amp and 40 Amp Inductive Loads.